We are developing the social individualist meta-context for the future. From the very serious to the extremely frivolous... lets see what is on the mind of the Samizdata people.
Samizdata, derived from Samizdat /n. - a system of clandestine publication of banned literature in the USSR [Russ.,= self-publishing house]
|
Twenty years ago it was simple: to any problem, freedom was the answer. But in recent years I have become less sanguine. Some might say I have grown up. Still, I have this uneasy feeling that Western societies are beset with problems and that freedom is not always the answer.
I thought what I would do was to write down the biggest problems facing us here in Britain, write down the libertarian approach and assess in a blog post if it would be successful or not. Well, like many of my big ideas that soon ran into the buffers of indolence. But I did manage to identify what I think are the biggest problems – or crises as I call them – that we face. They are (in approximate order of importance):
1. The Freedom of Speech Crisis. Cancel culture, de-banking, lawfare and actual punishment are being used to prevent people from expressing their opinions. Much of this is being done in the nominally private sector. If this continues the results will be disastrous.
2. The Integration Crisis. Hundreds of thousands of people live in this country and have no affection for its people or its customs and more are coming every day. This is a recipe for an Ulster on the grand scale.
3. The Debt Crisis. Government spending is unsustainable. Mind you, I was thinking that 15 years ago.
4. The Housing Crisis. Young people cannot afford a home where they can bring up children.
5. The Net Zero Crisis. OK, this hasn’t happened yet but when the electricity goes off, modern society will come to a halt.
6. The Ukraine Crisis. Well, you can add in Israel, Taiwan and probably a few other places too. The West is under military attack by people who would like to see it destroyed.
7. The NHS Crisis. Long waits for poor care and indifferent service.
There are a couple that tend to get mentioned regularly that I haven’t included. The Migration Crisis is really part of the Integration Crisis and part of the Housing Crisis. Wokery is part of the Integration Crisis (again) and also part of the Freedom of Speech Crisis.
People occasionally mention the Population Crisis – not enough babies being born. I tend to think this is either not a problem at all (the market will sort it out) or something that is beyond politics.
Is there anything I’ve missed? Do libertarians have the answer?
Earlier this week three girls were stabbed to death in Southport. Several others are still in hospital. A 17-year-old of foreign ancestry has been arrested. This has led to protests which in turn have led to disorder. The communist establishment has blamed the disorder on “far right” outsiders. Given how widespread the protests/riots have become we will soon have to conclude that the whole of the British “far right” live at 10A Acacia Terrace, Nether Wallop.
So, who are these “far right”-ists? Well given how often Tommy Robinson and his supporters are labelled “far right” it would seem that either of the two demos he has organised in London this year would be good places to find out. As it happens I attended both of them.
Both times I drafted but didn’t publish a light-hearted piece for Samizdata. For the second – which took place what seems a very long week ago – I imagined what a Nazi might make of it. The long and the short of it was not much but given the events of this week it didn’t seem appropriate to post it.
Given the crowd and their flags one would have to conclude that the “far right” are people who are proud of their countries of origin whether they be England, Wales, Scotland, Ireland (both bits) or Britain as a whole, Canada, Israel or pre-revolutionary Iran. One would also have to conclude that many are far from the stereotypical pissed-up, white, working-class male.
Given the speakers one would have to conclude that they are extremely sceptical about mass migration, deeply suspicious about the way the law is being administered, in favour of freedom of speech, pro-Christian, mostly Reform voters and of all the colours and sexes under the sun.
And very, very angry.
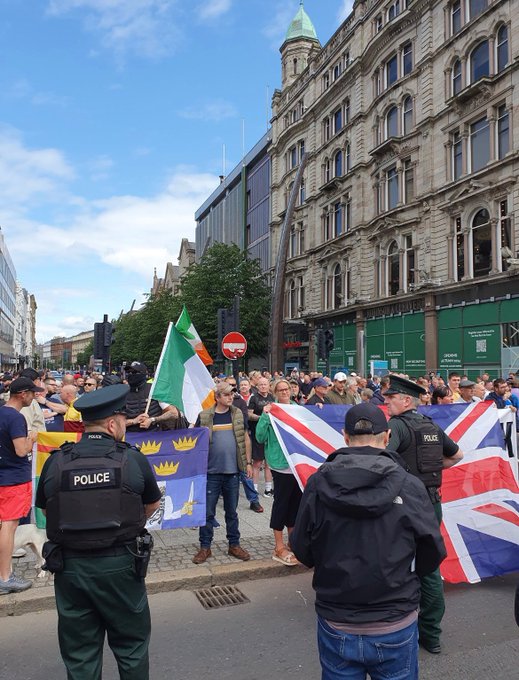 Belfast today. Is there nothing the far right cannot do? Update I have taken on board Mr Ed’s quite correct comments and kicked myself appropriately. And Natalie’s too. The use of the word “foreigner” is, I accept, contentious.
Natalie writes,
That loss of trust is one of the things that has made me much less pro-immigration than I once was. If that means the loss of my Libertarian purity certificate, so be it.
Amen to that. For years I have been trying to reconcile my belief in freedom with my doubts about immigration and have totally failed.
I would prefer not to lose my Libertarian purity certificate. I want a political philosophy that is simple and has universal application. That way I don’t have to think too hard. For the last 30 years libertarianism has been that philosophy. Name an issue of the day and I can give you the answer. Sluggish growth? Privatise, lower taxes and de-regulate. Busy roads? Privatise. Inflation? Abolish the Bank of England or re-introduce the Gold Standard, or, er… privatise the Bank of England. OK, some issues are not quite that easy but usually they are. Until we get to immigration. Because if libertarianism means open borders then libertarianism is wrong because open borders are a disaster.
→ Continue reading: Immigration and the libertarian
The Labour government that will take office tomorrow will be a disaster. Keir Starmer will make a terrible prime minister – a political weathervane, swinging wildly towards the policies he thinks will be most popular; a weak, unimaginative leader trying to keep the lid on a party seething with far-left lunatics, bitter class warriors, anti-Semitic bigots and deranged wokels.
– Fergus Mason
Once upon a time we had God. God was someone to emulate; someone whose rules one should attempt to live by. Nowadays, in our secular age, we have anti-God a.k.a. Hitler. Hitler is all bad and we should do the precise opposite of what he said and did.
But is that the case? How bad would things be if Hitler were in charge?
It would not be great for freedom of speech. But then right now is not great for freedom of speech. It would not be great for Jews. But then right now is not great for Jews. And they do, at least, have somewhere to go nowadays.
He might want to start a world war. But he would be frustrated because we are already in a world war. But I think we can be pretty sure he would prosecute that war with rather more vigour than our current masters can muster.
Economically speaking, he would be a disaster. He is, after all, a socialist. He would do nothing about the debt, he would reduce trade and be constantly trying to pick winners. So not much change there. A lot would depend on how enthusiastically he embraced Net Zero. Nazis were appalling environmentalists. I suspect, however, that so long as there was a war to fight that would take priority.
I think we can be pretty sure that the small boats crisis would come to an end. The Volksmarine machine-gunning anyone in a small boat would be likely to put a damper on the people-smugglng trade. Similarly, I don’t think he’d have much time for illegal migration. Or legal migration for that matter. Quite the opposite. Fewer people around would mean lower house prices. So, that’s a Hitler win. Unfortunately, Hitler’s socialist economics would mean shortages of all sorts of things. So, you’d have a house but it wouldn’t have any windows.
He might initially have some trouble with activist judges. But given that he will have a majority in Parliament – Nazis are quite good at arranging that sort of thing – and given that via the Bill of Attainder, Parliament can execute anyone they don’t like without giving reasons, I don’t think the judges would prove much of an obstacle.
I don’t think he would have much time for DEI (or DIE as think we ought to start calling it) or the whole equality agenda. At very least that’s good news for the Garrick Club, if it can retain any degree of independence. OK, so the members would have to sing the Horst Wessel Lied every evening but who doesn’t like a good sing song every now and then? Especially, if it’s being led by prominent celebrities.
On that point, it would certainly be amusing to watch as the gobshites at the BBC and elsewhere in the establishment, heaped praise on the new government, claiming that it was their idea all along in their vain attempts to secure a party membership.
Communist indoctrination in universities would come to an end. To be sure it would be replaced by a different form of indoctrination but at least white men would not be being taught to hate themselves.
I don’t think he’d have a lot of time for Islamic terrorism or Islam in general. I think he’d put likely trouble-makers in concentration camps. Most would fall foul of his racial policies.
Art and aesthetics generally would be better. Who wouldn’t enjoy the sight of the Angel of the North being melted down to make 155mm shells? The remake of Love Thy Neighbour would be compulsory viewing. Literally.
The key thing is that by shifting the Overton Window, Hitler would be able to cut the Gordian Knot that makes doing anything at the moment almost impossible. It is amazing what you can achieve when you are prepared to lock up your opponents.
At this point, I should point out that a Hitler government may well turn out to be sub-optimal. But given the path towards an Islamo-communist tyranny we are currently on one would have to say it could be worse.
As readers may remember, I am a big fan of Denys Davydov, the Ukrainian podcaster. Almost every day since US aid to Ukraine was turned off by Congress, Denys has been slagging off President Trump. Some of the language! His claim is that Trump is behind this block and that he wills a Russian victory. A couple of months ago, I checked on a Trump speech and although he wasn’t clearcut in what he intended to do it was clear that the Trump-is-a-Putin-pawn narrative was just nonsense.
Today he posted this (helpfully re-posted by Ukraine detractors.)
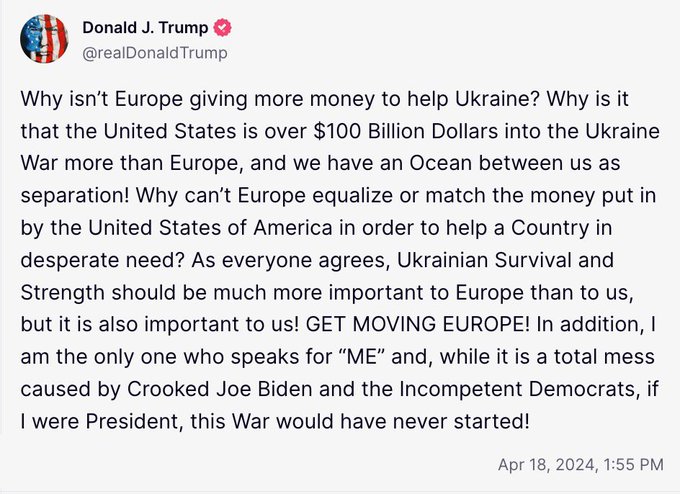
Look at what he is actually bloody-well saying! “…a Country in desperate need.” “…Ukrainian Survival and Strength…” Does that sound like someone who is indifferent to Ukraine’s fate?
“Why can’t Europe equalize or match the money put in by the United States of America…”
Assuming that European aid is indeed less than America’s, well, why can’t Europe match America’s expenditure? If Europeans don’t think Ukraine is worth defending why should the US pick up the slack?
Assuming Trump gets elected this is what I think he’ll do. He will make some offer to Putin. Something along the lines of, keep Crimea, lose the Donbass. Putin will reject it and then Trump will kick the living covfefe out of the bastard.
I have one policy on the royals: do not actively seek out information on them. I do not believe that I am going to learn anything particularly useful by following their doings.
But you cannot avoid finding things about them passively. In recent months the following facts have unwontedly entered my conciousness:
- The King has cancer
- The Princess of Wales was in hospital for a long time
- The Princess of Wales has not been seen in public for a long time
- The Princess of Wales issued a doctored image of herself and her children
- The claim is going round that the Princess of Wales doctored the image herself
My theory is that the Princess is extremely unwell and that the Palace is trying to cover things up. But why? Well, they can be a bit odd when it comes to Royal health. I mean the Queen one day accepting the resignation of one Prime Minister, appointing another, having a photo taken of the event with her standing upright no less and dying two days later is pretty dramatic. And is a little bit suspicious. You do get the impression that we are not being told the full story. A similar impression was given with the Queen Mother – as was – who was forever ending up in hospital with a fish bone stuck in her throat. Always – seemingly – on a Friday night.
And so with this. Do they really think that an essential part of keeping the Royal show on the road is maintaining an image of – how to put it? – invulnerability? Well, they’ve blown that when it comes to the King, so why maintain the pretense when it comes to the future Queen?
Maybe, they’re just stupid.
By the way and for what it is worth, I thought the doctoring was pretty good. So good that I couldn’t figure out what had been doctored.
Update 13/3/24 Top fact-free speculation here from Toby Young. Starts at the 57:53 mark.
I think it’s about time we mentioned that the Steyn v Mann defamation trial is currently taking place in Washington D.C.. For those who have forgotten – or never knew in the first place – this concerns articles that Mark Steyn and his co-defendent blogger Rand Simburg wrote twelve years ago accusing university employee Michael Mann of fraud in scientific research.
This is the first time the Hockey Stick graph – which suggested a dramatic and unprecedented rise in global temperatures – has been subject to judicial examination.
If you want to follow daily proceedings you might like to check out the Climate Science on Trial podcast hosted by Phelim McAleer and Ann McIlhenny.
We are constantly being told by that coalition of communists and racists that talk about “de-colonisation” that the British Empire was a Bad Thing and that therefore we whiteys should a) be ashamed, b) tear down any monuments to that empire and c) give all our money and wealth to the descendents of the alleged victims of that empire. This despite the fact that there is almost no one alive who had anything to do with said empire. There is no force for good like inter-generational guilt.
For some time Oxford Academic Nigel Biggar has been discomfited by this claim and these demands. In 2017, he was denounced by “fellow” academics for running an “Empire and Ethics” project. Last year saw the publication of his book Colonialism: A Moral Reckoning. This itself was something of a palaver with Biggar’s original publisher dropping the thing in what appeared to be a cancellation. Luckily there is still some competition in the publishing world and another publisher came to the rescue.
Biggar is at pains to point out that he is an ethicist not a historian. He deals in moral issues not historical ones; hence the title of the book. Well, that’s the theory but with over a hundred pages of footnotes it would appear he is quite good at the not-day job.
He examines the various claims that the “de-colonisers” make: Amritsar, slavery, Benin, Boer War, Irish famine. In all cases he finds that their claims are either entirely ungrounded or lack vital information that would cast events in a very different light.. Amritsar? Dyer was dealing with political violence that had led to murder. Some victims had been set alight. Anyway, he was condemned for his actions by the British authorities and, indeed, his own standing orders. Slavery? Everyone had it and Britain was the first to get rid of it. Benin? They had killed unarmed ambassadors. Irish famine? They tried to relieve it but they were quite unequal to the size of the task. In the case of Benin he comes very close to accusing the leading de-coloniser of knowingly lying. The only one of these where I don’t think he is so convincing is the Boer War. He claims that Britain was concerned about the future of the Cape and especially the Simonstown naval base and also black rights. I think it was the pursuit of gold even if it does mean agreeing with the communist Eric Hobsbawm.
He is far too polite about the “de-colonisers”. They are desperate to hammer the square peg of reality into their round-hole of a theory. To this end they claim knowledge they don’t have, gloss over inconvenient facts, erect theories that don’t bear scrutiny and when all else fails: lie. Biggar tackles all of these offences against objectivity with a calmness and a politeness that you can bet his detractors would never return.
The communists – because they are obsessed with such things and are past masters at projection – like to claim that there was an “ideology” of Empire. Biggar thinks this is nonsense. As he says:
There was no essential motive or set of motives that drove the British Empire. The reasons why the British built an empire were many and various. They differed between trader, migrant, soldier, missionary, entrepreneur, financier, government official and statesman. They sometimes differed between London, Cairo, Cape Town and Calcutta. And all of the motives I have unearthed in this chapter were, in themselves, innocent: the aversion to poverty and persecution, the yearning for a better life, the desire to make one’s way in the world, the duty to satisfy shareholders, the lure of adventure, cultural curiosity, the need to make peace and keep it, the concomitant need to maintain martial prestige, the imperative of gaining military or political advantage over enemies and rivals, and the vocation to lift oppression and establish stable self-government. There is nothing morally wrong with any of these. Indeed, the last one is morally admirable.
One of the benefits of the British Empire is that it tended to put a stop to local wars. How many people lived because of that? But that leads us on to another aspect. Almost no one ever considers what went on before the Empire arrived. Was it better or worse than went before it? Given that places like Benin indulged in human sacrifice, I would say that in many cases the British Empire was an improvement. And if we are going to talk about what went before what about afterwards? He has little to say about what newly-independent countries have done with their independence. The United States, the “white” (for want of a better term) Commonwealth and Singapore have done reasonably well. Ireland is sub-par but OK. Africa, the Caribbean and the Indian sub-continent have very little to show for themselves. This may explain why Britain needed very few people to maintain the Empire. At one point he points out that at the height of the Raj the ratio of Briton to native was 1 to 1000. That implies a lot of consent. Tyrannies need a lot more people.
The truth of the matter is that talk of reparations is rooted in the failure of de-colonisation. If Jamaica were a nicer place to live than the UK, if Jamaica had a small boats crisis rather than the UK then no one would be breathing a word about reparations or colonial guilt. All this talk is pure deflection from the failure of local despots to make the lives of their subjects better.
Biggar has nothing to say about what came after the empire and he also has little to say about how it came about in the first place – so I’ll fill in that gap. Britain acquired an empire because it could. Britain was able to acquire an Empire because it mastered the technologies needed to do it to a higher level and on a greater scale than anyone else. Britain mastered technology because it made it possible to prosper by creating wealth. That in itself was a moral achievement.
Of course, modern Britons don’t actually need to justify the Empire. As I pointed out at the beginning none of us had anything to do with it. You could argue (does anyone actually do this?) that we current-day Britons are the inheritors of the same culture and perhaps we should be ashamed about that. Except that I am not in the mood to condemn a culture that produced the rule of law, freedom of speech, property rights and the Industrial Revolution. Anyway, does anyone seriously think that modern British culture would be capable of giving birth to a second empire? Culture changes. The other argument is that many of us continue to be the beneficiaries of the Empire. At very least those who have started with nothing and yet are still on the hook for reparations are entitled to feel a bit miffed. But one only has to look around to see that most of Britain’s prosperity is much more recent in origin. Sure, that big house might have originally been built from a slaver’s profits but if a more recent person hadn’t kept the roof intact it would be a ruin by now.
A narrative about a rapacious British Empire is being used to first humiliate and shame modern Britons in preparation for their impoverishment and eventual extermination. OK, maybe I am getting ahead of myself here but I’ll bet you some of them of thinking that. There is certainly nothing in the “decolonisation” belief system to prevent it. Biggar’s achievement is to demonstrate that – if you do believe in intergenerational guilt – there is nothing to be ashamed of.
Javier Milei, President of Argentina, is a very odd person. He has four dogs. Now, you may think there is nothing particularly odd about that. But these dogs are clones. They are clones of the late Conan, Milei’s first mastiff, who was named after Conan the Destroyer. The clones are named Murray, Milton, Robert and Lucas apparently after famous economists. Sadly, they are not so famous to me. Yes, Murray is doubtless Murray Rothbard and Milton, Milton Friedman – men who incidentally did not necessarily see eye to eye on monetary matters – but otherwise I am stumped. Robert? Surely not Skidelsky? Lucas? A complete blank. And no Adam, Ludwig, Friedrich or Henry? Truly Milei is an odd person.
Tommy Robinson. EDL. English Defence League. Racists. Racism. Racist. Case closed, yes?
A few years ago at a loose end – in full knowledge that the above was true – I was browsing YouTube and I came across an interview with the man. I pressed play. Almost the first thing he said was something like, “I am not the person people think I am.” That seemed interesting – challenge your beliefs and all that – so I listened further. Boy, was I in for a shock. Since then I’ve read his book, Enemy of the State – available from obscure retailers – and followed him on obscure social media platforms. This is what I have gleaned:
- For a racist he has a suspiciously large number of black friends.
- For a racist he has a suspiciously large number of Jewish friends.
- He even has a Muslim friend.
- He doesn’t seem to like racists much, even telling them to **** *** out of his comments and burning their flags.
- They don’t seem to like him much, sometimes claiming that he is a Mossad agent.
- His main argument is that mass migration in general and large-scale Muslim immigration in particular represent a threat to Britain and the British.
- He utterly hates the police. A lot of this springs from an incident when (so he claims) he was attacked by an off-duty officer who subsequently lied in court. But there are plenty of other cases outlined in his book.
So why the hate? Or to put it another way, why does Robinson attract hate in a way that Douglas Murray does not despite the two having almost identical political views? I can’t help thinking that a lot of this is to do with class. In accent, dress and associates Robinson is unapologetically – for want of a better term – working class . It would appear that a lot of the MSM etc have much the same attitude to the working class as they do to ethnic minorities: they should be seen and not heard. They should accept the opinions that have been assigned to them and be grateful.
Another explanation lies in – how shall I put this? – his general attitude to authority. Take yesterday, for instance. An “Against Anti-semitism” march was being held in Central London. Robinson encouraged people to go along. The organisers – because they know nothing about the man and think that attempting to curry favour with the MSM is something other than a fool’s errand – stated that his presence would not be welcome. He went along anyway. The police arrested him. The police’s actions were, of course, disgraceful but Robinson resisted arrest and got a face full of pepper spray for his trouble.
A further explanation lies in what might be described as “information management.” Robinson believes – as do I – that actions speak louder than words. So, he doesn’t believe he has to defend himself when smeared; his actions will speak for themselves. Except that – so far – they haven’t. This means that he hasn’t gone to the trouble of organising a defence of his beliefs in an easily retrievable manner. My gleanings above are the result of years of followship. His book is also terribly organised.
 Robinson is the one on the left. The guy on the right is long-time political ally Danny Roscoe.
By some miraculous and tortuous process you have become your country’s head of government and been endowed with dictatorial powers. What is the first thing you do?
|
Who Are We? The Samizdata people are a bunch of sinister and heavily armed globalist illuminati who seek to infect the entire world with the values of personal liberty and several property. Amongst our many crimes is a sense of humour and the intermittent use of British spelling.
We are also a varied group made up of social individualists, classical liberals, whigs, libertarians, extropians, futurists, ‘Porcupines’, Karl Popper fetishists, recovering neo-conservatives, crazed Ayn Rand worshipers, over-caffeinated Virginia Postrel devotees, witty Frédéric Bastiat wannabes, cypherpunks, minarchists, kritarchists and wild-eyed anarcho-capitalists from Britain, North America, Australia and Europe.
|






